Overview
QQube provides out-of-the-box ability to drag and drop fields into Excel using the Select Assistant from the QQube Add-In for Excel. It comes free with QQube, and hides the complexities of dealing with raw tables and relationships.
Advanced users will recognize that the Excel Add-In is a "front-end" for MSQuery, giving them the power to see and use the underlying data queries.
Imputing Data vs Dynamic Interaction with a Database
Excel is still the tool of choice for data manipulation for the most recent generation. However, it may be argued that it is not a report writer - and was never designed to be. Especially when compared against powerful report writing applications like SAP Crystal Reports.
Traditional Excel
In general, we use basic Excel functionality to impute data in disparate cells, and then create calculations. Advanced users avail themselves of array formulas, advanced macros, and VBA to achieve "report-like" results.

Excel Connected to a Database
The problem, however, is that data from any database - including QQube - is not dynamically connected to Excel in disparate cells. Rather the data exists in blocks of contiguous cells (see example below) where a filter or sort effects all of the information - not just one piece of it.

Even if you could bring in database information one cell at a time, each cell would have its own filtering mechanism and dependency; something that would drive you crazy if you had to filter 10,000 individual cells, one at a time.
How QQube Interacts with Excel
Dynamic Range
Here is an example of a Dynamic Range populated from the QQube Select Assistant, which is available from the QQube Excel Add-In Ribbon.

Pivot Table
Here is an example of a Pivot Table also populated from the QQube Select Assistant. In this instance there are two steps: one step to the select the field(s) you want, and the second to move the field in the proper pivot table quadrant.
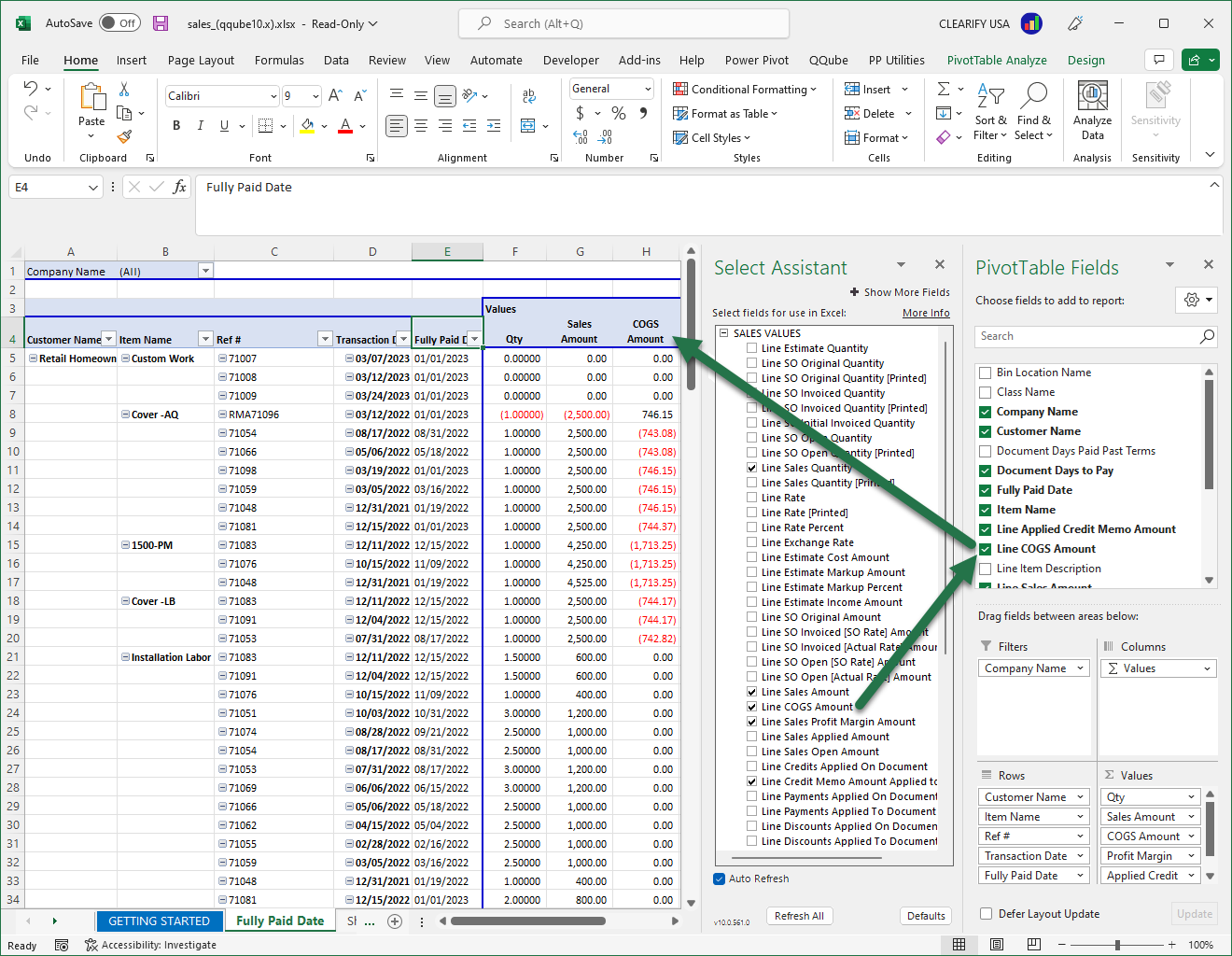
Pivot Tables Overcome Limitations of Dynamic Lists in Excel
Dynamic Lists
Automatically get updated regardless of whether the number of rows changes or not. You can do sorting and advanced filtering. The one thing you can't do is create subtotals (Data Tab in Excel)

Dynamic Pivot Tables
Auto subtotals upon demand, as you add or re-arrange row labels (Dimension Fields) and is arguably the easiest form of data analysis in Excel.
There are two functional limitations however:
- You can't create a calculated column that represents a subset of data (only available in PowerPivot)
- Labels must be in the first left most columns, e.g. dimension name like customer, item, account, and all measures must be placed in the right most columns.
Advanced Capabilities Beyond Excel
To create advanced data models with QQube, consider using either PowerPivot, or Power BI.
With respect to Excel's capabilities, inventory data models are more suited to PowerPivot, because you can create calculations that not only show what is on hand, but you can simultaneously display sales or consumption columns with varying date range categories. These are just not possible in a regular Pivot Table.
Power BI gives a graphical interpretation that goes beyond PowerPivot - and even gives you traditional column and row display and functionality - the best of both worlds.
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article